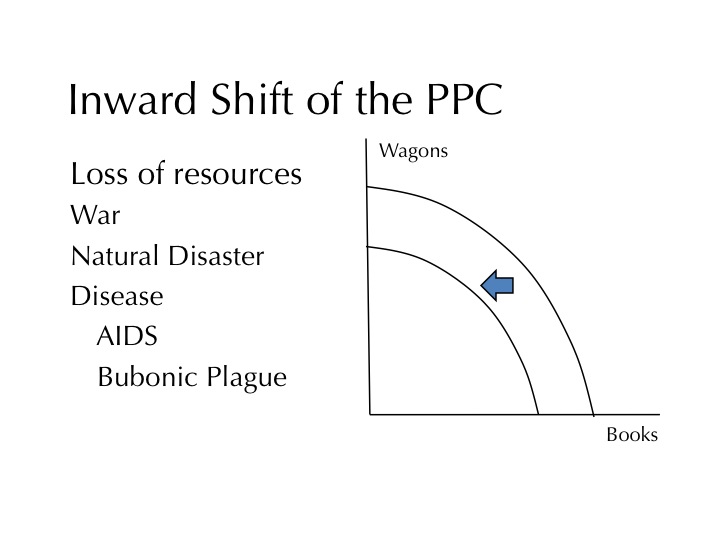
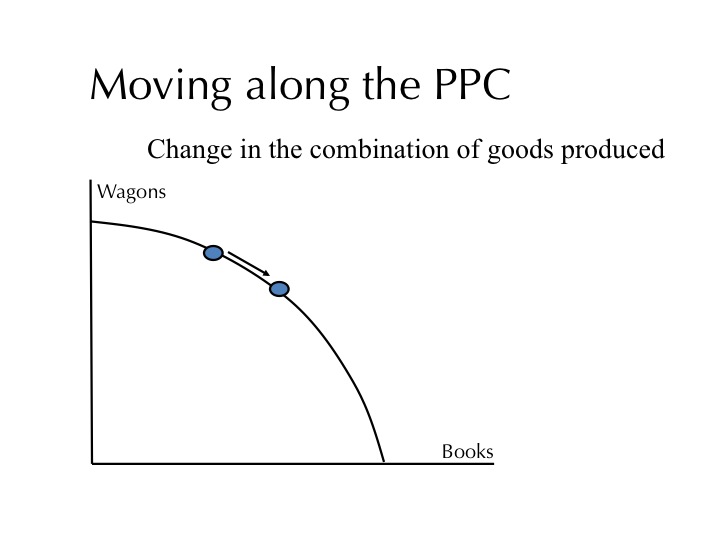
Tuesday, January 24, 2017
Important Formulas for Supply
- Fixed Cost: Cost that does not change no matter how much of a good is produced
- Variable cost: Cost that rises or falls depending upon how much is produced. ex: electricity bill.
- TFC + TVC = TC
- AFC + AVC = ATC
- TFC/ Q = AFC
- TVC/ Q = AVC
- TC/ Q = ATC
- AFC x Q = TFC
- AVC x Q = TVC
- marginal cost = new TC - old TC
Q = quantity
TFC = total fixed cost
TVC= total variable cost
TC = total cost
MC = marginal cost
AFC = average fixed cost
AVC = average variable cost
ATC = average total cost
January 20 2017
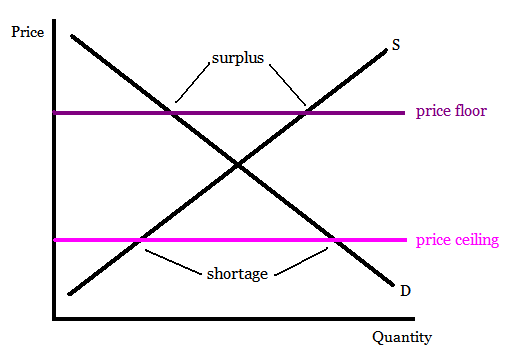
Excess Demand
Excess Demand
Excess demand: quantity demanded is greater than quantity supplied (shortage). Ex: flu shots at Walgreen's
Shortage: consumers can't get quantity of items they desire
Equilibrium: Point at which supply/demand curve intercept
Price ceiling: occurs when government puts a legal limit on how high the price of a product can be. (must be set below the equilibrium mark to be efficient)
Excess supply: quantity supplied is greater than quantity demanded (surplus)
Surplus: when the producers have inventory they can't get rid of.
Price Floor: Lowest legal price a commodity can be sold at. (Used by government to prevent prices from becoming too low) ex: minimum wage.

January 11, 2017
Elasticity of Demand
Elasticity of demand: Measure of how consumers react to a change in price.
Elastic demand
- Demand that is very sensitive to a change in price
- Product is not a necessity
- Always greater than 1
- Available substitutes
- Example: soda, coats, steak
Inelastic demand
- Demand that is not very sensitive to a change in price
- Product is a necessity
- Few/ no substitutes
- Less than one
- Example: gas, insulin
Unitary elastic
- Equal to one (in a perfect society)
Total Revenue: total amount of money a company receives from selling goods and services.
Formula: Price x Quantity
January 3, 2017
Macroeconomics- The study of economy as a whole
Positive economics: claims attempt to describe the world as is. Very descriptive in nature. Fact-based
Normative economics: claims attempt to describe how the world should be. Opinion based.
Needs vs. Wants
Needs: basic requirements for survival
Wants: desires
Scarcity vs. Shortage
Scarcity: fundamental economic problem that all societies face. How to satisfy unlimited wants with limited resources.
Shortage: quantity demand it exceeds quantity supplied.
Goods vs. Services
Goods: tangible (touchable) commodities. Capital/consumer goods. Capital goods are items used in creation of other goods. Consumer goods are goods intended for use by consumer.
Services: work that is performed for someone. ex: entertainment, getting haircut, etc.
Two Types of Efficiency
- Productive- Products are being produced in the least costly way. Any point on the PPC
- Allocative- Products being produced are the ones most desired by society
January 4, 2017
Factors Of Production
- Land: natural resources
- Labor
- Capital (human/ physical) human: when ppl acquire skills and knowledge through experience/education. Physical: money, tools, buildings, machinery etc
- Entrepreneurship: involves risk taking, being inventive/innovative. Takes 3 factors of production to promote the business.
Trade-offs: alternative we sacrifice when we make a decision
Opportunity cost: next best alternative
Guns or butter: trade-offs a country faces when choosing whether to produce more or less of military goods or consumer goods
Thinking at the margins: deciding whether to add/subtract one additional unit of some resource
Efficiency: using resources in such a way to maximize production of goods/services. Increases profits
Under-utilization: opposite of efficiency. Using fewer resources, leads to decreased profits.
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)